The key to becoming a more successful PR specialist lies in mastering both practical and theoretical aspects. Theories and models, derived from observed practices, serve as valuable tools for predicting outcomes. They play a crucial role in the comprehensive research and meticulous planning required for designing and executing effective public relations campaigns. This article explores two PR theories – excellence and two-step flow theory – along with three PR models – RACE, two-way symmetrical, and PESO model. Familiarity with these theories and models can significantly enhance your ability to craft impactful public relations campaigns, including those tailored for platforms like Instagram.
Public Relations Theories
Excellence Theory
J. Grunig and L. Grunig (2008) formulated a set of public relations functions that contribute to effective organizational management. They define "excellence in public relations" as a collection of attributes and practices that facilitate the establishment of quality, long-term relationships with strategic constituencies (L. Grunig & J. Grunig, 2008). According to this theory, public relations plays a role in helping an organization adapt its internal and external environment to align with its desired behavior. The theory also emphasizes symmetrical communication to manage relationships between the internal and external environments and organizations more effectively. The Excellence theory introduces the two-way symmetrical model of public relations, focusing on ensuring that organizational decisions are mutually beneficial for both the organization and its audiences. Further details about this model can be found in the section on Public Relation Models.
Two-Step Flow Theory
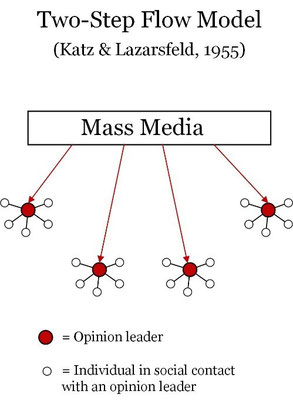
The Two-Step Flow theory, originally proposed by Paul Lazarsfeld in 1944 and later expanded by him and Elihu Katz in 1955, seeks to elucidate how the media can impact audience behaviors and beliefs. According to this theory, the media does not directly influence the audience but is instead utilized to inform opinion leaders, also known as thought leaders or influencers, who wield significant influence in persuading people to change their attitudes and behaviors. The first step involves the media conveying its message to the opinion leader, and the second step occurs when the opinion leader transmits the message to the audience (Fig.1).
When opinion leaders transmit a media message, they often incorporate their own opinions and interpret the original content based on their understanding. Additionally, they share similarities with the audience they seek to influence. Although the original theory focused more on word-of-mouth conversations between opinion leaders and audiences, contemporary discussions of such interactions now take place on social media platforms like Facebook or Instagram (Kuchta, 2017). Instagram influencers with substantial followings possess the ability to influence and persuade their audience by engaging with them on a more personal level, lending authenticity and credibility to the communication.
Public Relations Models
RACE Model
The RACE model, developed by John Marston in 1963, is an acronym representing the key components of research, action planning, communication, and evaluation (Creative Commons, 2012). This model serves as a strategic framework for devising a comprehensive public relations plan (Fig.2).
- Research is used to analzye a situation or challenge confronting an organization, aiming to articulate a problem or opportunity in a manner that directs public relations efforts toward resolving the issue.
- An action plan is developed to tackle the issue identified in the research phase. The primary emphasis during this stage is on determining the optimal course of action to deal with the issue.
- The public relations plan is then implemented through the use of communication tools designed to achieve the primary objectives.
- During the evaluation stage, the achievement of set objectives is measured and analyzed.
Two-way Symmetrical PR Model
Grunig and Hunt (1984) outline four models of public relations, and the most relevant for this article is the fourth model – the two-way symmetrical PR. This model advocates for dialogue and emphasizes the equilibrium of power relationships. With the advent of social media as a prominent platform for public relations, this model is gaining significance.
According to Grunig (2013), "digital communication makes symmetrical communication fairly easy to practice and, in fact, might make it unavoidable. With digital communication, publics have much more control over their sources of information, and organizations have little choice other than to communicate with them symmetrically." For instance, organizations leverage platforms like Instagram to engage and communicate with current and potential customers. Users also wield the power to influence organizations by expressing their opinions, visible to a broader audience.
PESO Model
The model facilitates the categorization of all the company’s digital channels into specific groups, offering insights into how these media types can be utilized in the Instagram strategy. Definitions of the four media types, along with examples, are provided below (Bartholomew, 2010):
- Paid media encompasses all types of content for which the company pays, and that appears on third-party channels. Examples of paid media include Facebook ads, promoted tweets, sponsored Instagram posts, banner or display advertisements, pay-per-click programs, and advertorials.
- Earned media comprises traditional media outreach and blogger/influencer relations aimed at encouraging third-party content providers to promote a brand, content, products, and services. This category includes influencer reviews, traditional public relations, and media relations.
- Shared media involves shares received on various social media networks, encompassing shares on platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and others.
- Owned media comprises all web properties owned by a company, encompassing websites, blogs, email, microsites, apps, and user-generated content.
Bibliography:
- Bartholomew, D. (2017). The Digitization of Research and Measurement in Public Relations. [online] Social Media Explorer. Available at: http://socialmediaexplorer.com/online-public-relations/the-digitization-of-research-and-measurement-in-public-relations/ [Accessed 11 Dec. 2017].
- Dietrich, G. (2014). Spin Sucks: Communication and Reputation Management in the Digital Age. Que Publishing (1859).
- Grunig, J. E. (2008). Excellence theory in public relations. In. W. Donsbach (Ed.), The International Encyclopedia of Communication, Volume 4 (pp. 1620-1622)
- Grunig, J. and Hunt, T. (1984). Managing Public Relations. New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
- James Grunig: Excellence Theory. (2017). The Two-Way Symmetrical Model of Communication. [online] Available at: https://excellencetheory.wordpress.com/2013/09/27/the-two-way-symmetrical-model-of-communication/ [Accessed 8 Dec. 2017].
- Katz, E., & Lazarsfeld, P. (1955). Personal Influence. New York: The Free Press.
- Kuchta, L. (2017). Two-Step Flow Communication Model | Study.com. [online] Available at: https://study.com/academy/lesson/two-step-flow-communication-model.html [Accessed 12 Dec. 2017].

Written by Liudmila Kazak